Introduction With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) and the proliferation of connected devices, there has
been a significant increase in the amount of data being generated. This has led
to a surge in demand for faster and more efficient ways of processing and analyzing
data. Edge computing has emerged as a solution to this problem. In this blog
post, we will explore what edge computing is, how it works, and its advantages
and disadvantages.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a
distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer
to the location where it is needed, i.e., at the edge of the network. In
contrast to traditional cloud computing, which centralizes computation and data
storage in large data centers, edge computing pushes the computation and
storage closer to the devices and users that generate and consume data.
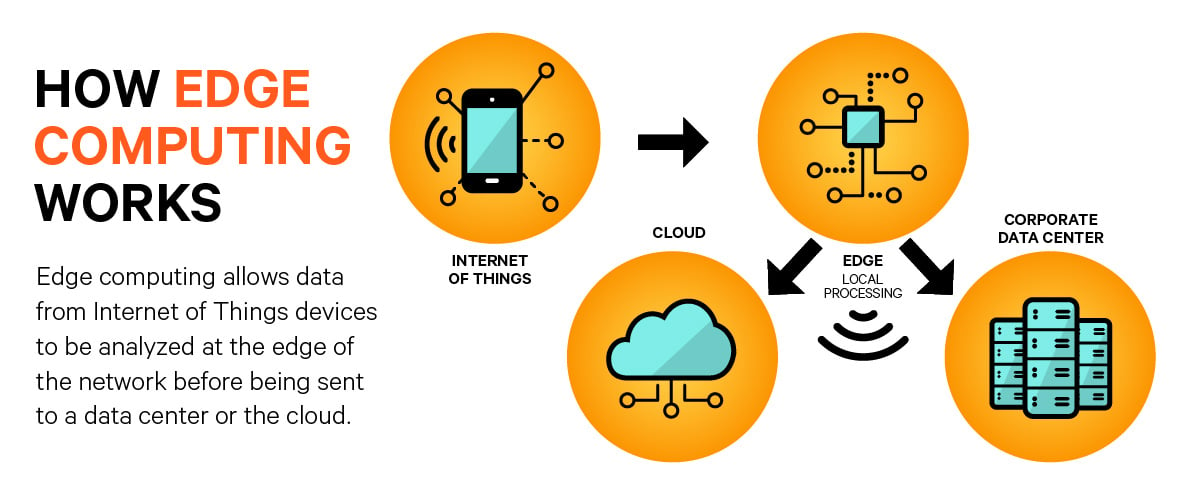
Edge computing aims to
reduce the latency and bandwidth requirements of traditional cloud computing by
processing and analyzing data locally, without the need to transmit it to a
remote data center. This is particularly useful in scenarios where the latency
and bandwidth requirements are high, such as in industrial automation,
autonomous vehicles, and augmented reality.
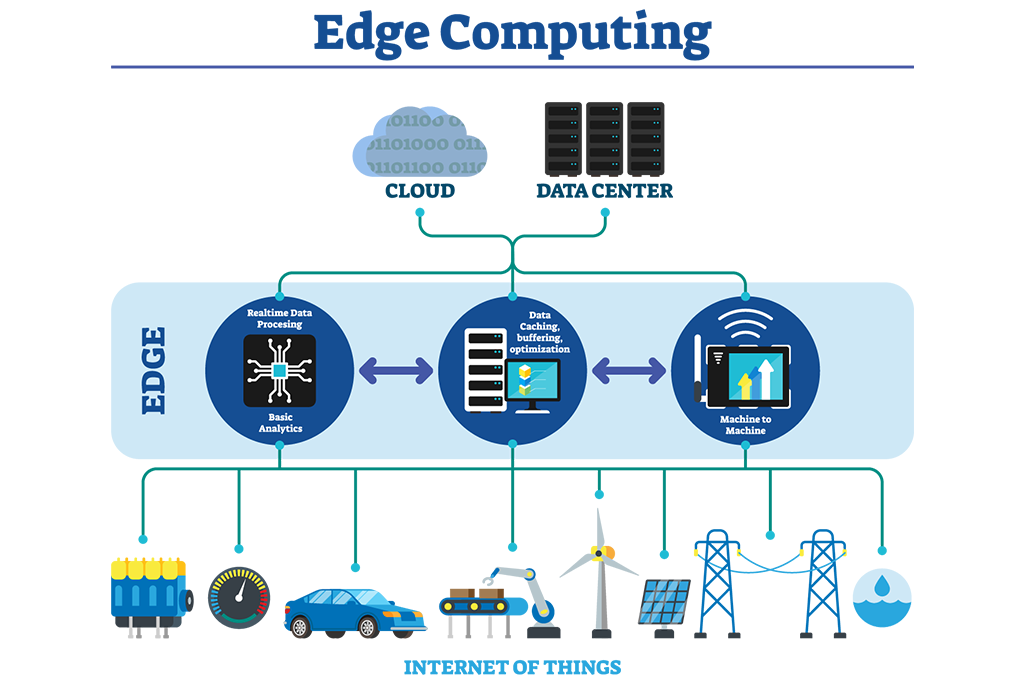
How does Edge Computing work?
Edge computing involves a
distributed architecture that consists of three layers: the edge layer, the fog
layer, and the cloud layer. The edge layer is the outermost layer and consists
of the devices and sensors that generate data. The fog layer is the
intermediate layer and consists of edge computing nodes that are responsible
for processing and analyzing data. The cloud layer is the innermost layer and
consists of the traditional cloud computing infrastructure that is responsible
for storing and managing data.
The edge layer devices and
sensors collect data and send it to the fog layer nodes for processing and
analysis. The fog layer nodes are typically located in proximity to the edge
layer devices, and they are responsible for running real-time analytics and
decision-making algorithms on the data. The cloud layer provides additional
computational resources and storage for the fog layer, enabling it to scale up
and handle larger workloads.
Advantages of Edge
Computing
Reduced Latency: Edge computing can reduce the latency of
data processing and analysis by processing the data closer to the source. This
is particularly useful in scenarios where low latency is critical, such as in
industrial automation, where delays can have serious consequences.
Improved Security: Edge computing can improve the security of
data by reducing the need to transmit data to a remote data center. This
reduces the risk of data breaches and cyber attacks that can occur during data
transmission.
Increased Bandwidth: Edge computing can reduce the bandwidth
requirements of traditional cloud computing by processing data locally. This
can help to reduce the cost of transmitting data and improve the overall
efficiency of the network.
Scalability: Edge computing can provide scalability by
distributing the workload across multiple edge nodes. This enables the system
to handle larger workloads without overloading a single node.
Disadvantages of Edge
Computing
Complexity: Edge computing can be complex to implement due to
the distributed architecture and the need for specialized hardware and
software.
Cost: Edge computing can be more expensive than traditional
cloud computing due to the need for specialized hardware and software.
Management: Edge computing requires specialized management
tools and expertise to monitor and maintain the distributed architecture.
Security: Edge computing can increase the risk of security
breaches due to the distributed architecture and the need for specialized
security protocols.
Use Cases for Edge
Computing
Industrial Automation: Edge computing can be used to monitor
and control industrial processes in real-time, reducing the latency and
improving the overall efficiency of the system.
Autonomous Vehicles: Edge computing can be used to process
sensor data from autonomous vehicles in real-time, enabling them to make
real-time decisions and avoid collisions.
Augmented Reality: Edge computing can be used to process and
render augmented reality content in



.png)
.png)

0 Comments